Python API
The Python client provides a simple interface for co-simulation between Python and ProtoTwin Connect. You can install the Python client by running:
pip install prototwinClient
The Python client allows you to issue commands to load a ProtoTwin model, step the simulation forward by one timestep, read signals from ProtoTwin Connect, and write signals to ProtoTwin Connect. A basic example is provided below:
# STEP 1: Import the ProtoTwin client
import prototwin
import asyncio
import os
import math
# STEP 2: Define your signal addresses (obtain these from your ProtoTwin model)
simulation_time_address = 0
motor_target_position_address = 2
async def main():
# STEP 3: Start ProtoTwin Connect, load and initialize the model
client = await prototwin.start()
path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "BipedalRobot.ptm")
await client.load(path)
await client.initialize()
# STEP 4: Create the simulation loop
while True:
t = client.get(simulation_time_address) # Read signal value
client.set(motor_target_position_address, math.radians(45) * math.sin(t)) # Write signal value
await client.step() # Step the simulation forward by one timestep
asyncio.run(main()) # Run the simulation loopSignals
Signals represent IO for components defined in ProtoTwin. You can obtain the addresses for signals defined in ProtoTwin by opening the IO Browser and reading the addresses from the signals table.
Signals that have Write access (also called writable signals) can be written or read. Signals that have Read access (also called readable signals) can only be read. For example, it doesn’t make sense that you can write to the current force/torque reported by a motor component.
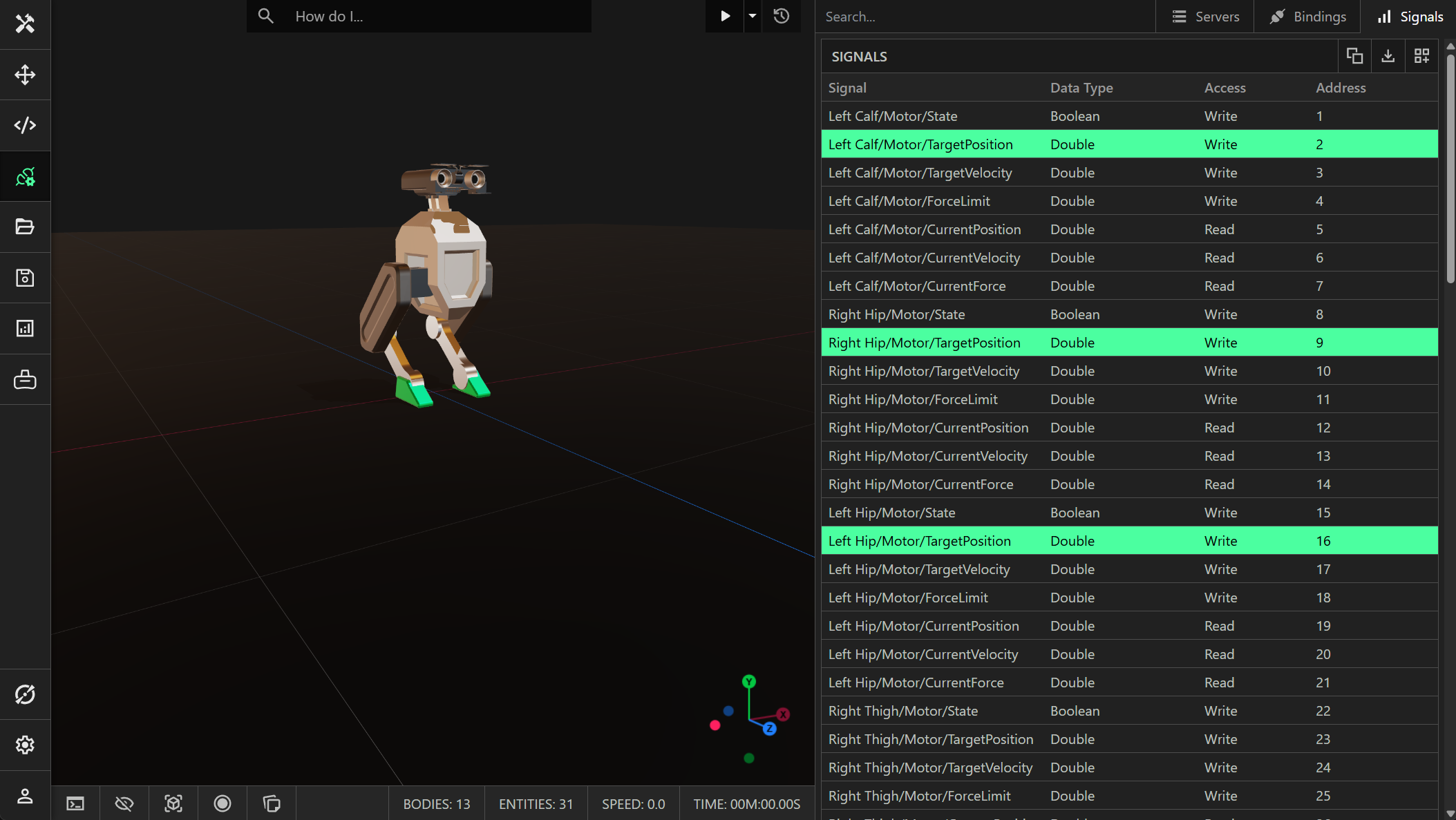
Signals have a strict data type and are defined by a Entity/Component/Property path. You can click the copy button to copy the selected signals to the clipboard. Use this to quickly create python variables for a signal. ProtoTwin will determine an appropriate name:
left_calf_motor_target_position = 2
right_hip_motor_target_position = 9
left_hip_motor_target_position = 16Types
Signals are strongly typed. The following value types are supported:
You can also find the signals provided by each component inside ProtoTwin under the I/O dropdown menu. Python does not natively support small integral types. The client will automatically clamp values to the range of the integral type. For example, attempting to set a signal of type UINT8 to the value 1000 will cause the value to be clamped to 255.
Sensors
ProtoTwin includes a number of built-in sensors that may be useful:
- Position Sensor
- Orientation Sensor
- Linear Velocity Sensor
- Angular Velocity Sensor
- Accelerometer
- Color Sensor
- Volumetric Sensor
- Distance Sensor
You can use these sensors to read the position, orientation, linear velocity, angular velocity, linear acceleration, etc from the digital world.
Custom IO
Many of the components built into ProtoTwin provide their own set of signals. However, it is also possible to create your own scripted components with their own set of signals. You can create a scripted component through the integrated script editor, or ask our AI assistant Torq to create a component for you. The example below demonstrates a custom component that exposes some IO, which can be used to measure the height of the Bipedal Robot’s feet above the floor:
import { type Entity, Component, DoubleSignal, Access, IO } from "prototwin";
export class HeightAboveFloorIO extends IO {
public height: DoubleSignal;
public constructor() {
super();
this.height = new DoubleSignal(0, Access.Readable); // Output (readable)
}
}
export class HeightAboveFloor extends Component {
#io: HeightAboveFloorIO;
public override get io(): HeightAboveFloorIO {
return this.#io;
}
public override set io(value: HeightAboveFloorIO) {
this.#io = value;
}
public get height(): number {
return this.#io.height.value;
}
constructor(entity: Entity) {
super(entity);
this.#io = new HeightAboveFloorIO();
}
public override update(dt: number) {
const bbox = this.entity.worldBoundingBox;
this.#io.height.value = Math.max(bbox.min.y, 0);
}
}Gymnasium Environment
We also provide a base environment for Gymnasium that can be used for robotics and reinforcement learning, where the robot is controlled by a neural network. You can install ProtoTwin Gymnasium by running the command:
pip install prototwin-gymnasiumProtoTwin Gymnasium also supports vectorized environments, allowing you to train AI models for many robots in parallel using the ProtoTwin Connect client. This allows you to train machine learning models much faster than using a single non-vectorized environment.