Motor
The motor component implements a servo motor, allowing for precise control of linear/angular position, linear/angular velocity and linear/angular acceleration. For more details on all properties associated with the motor component and how to use the motor component with scripting, please see the API documentation.
Prismatic, revolute and path joints may be driven by dynamic motors. You can select an existing motor to be bound to the joint, or click the add button next to the motor property to create a new motor component attached to the selected entity that is automatically bound to the joint. The motor component cannot be bound to a spherical or fixed joint.
The motor component implements an encoder, controller and stall detection. The encoder is used to measure the current position/velocity achieved by the motor. The controller implements a trapezoidal speed profile curve with constant acceleration and deceleration. The motor can stall if the force/torque limit is too little or if the rigid body collides with another rigid body. Stalls are detected when the stall tolerance is continuously exceeded for the duration of the stall timeout.
Properties
The motor component properties that are accessible through the inspector.
Type
The type of actuator used. It is one of the following values:
- Angular: An angular motor that produces rotary motion by applying a torque.
- Linear: A linear motor that produces linear motion by applying a force.
Controller
The module that controls the motor outputs. It is one of the following values:
- Position: Drives the motor from its current position to the target position.
- Velocity: Drives the motor from its current velocity to the target velocity.
Force Limit
The maximum torque/force that the motor can produce.
Current Position
The current position of the motor. This property can only be viewed through the inspector. The current position cannot be modified.
Current Velocity
The current velocity of the motor. This property can only be viewed through the inspector. The current velocity cannot be modified.
State
Whether the motor is powered on. A motor that is switched off applies no force/torque.
Target Position
The target position for the controller. This property is hidden when a velocity controller is used.
Target Velocity
The target maximum velocity for the controller.
Target Acceleration
The target acceleration for the controller.
Target Deceleration
The target deceleration for the controller.
Stalled
Whether the motor has stalled.
Action
The action that the controller should take when a stall is detected. It is one of the following values:
- None: The controller should not detect or act upon stalls.
- Stop: The controller should stop the motor when a stall is detected.
- Recover: The controller should attempt to automatically recover when a stall is detected.
Tolerance
The stall tolerance used by the controller to detect stalls. A stall is detected when the stall tolerance is continuously exceeded for the duration of the stall timeout.
Timeout
The stall timeout used by the controller to detect stalls. A stall is detected when the stall tolerance is continuously exceeded for the duration of the stall timeout.
IO
The IO signals for the motor component. Please see the MotorIO API documentation for more details.
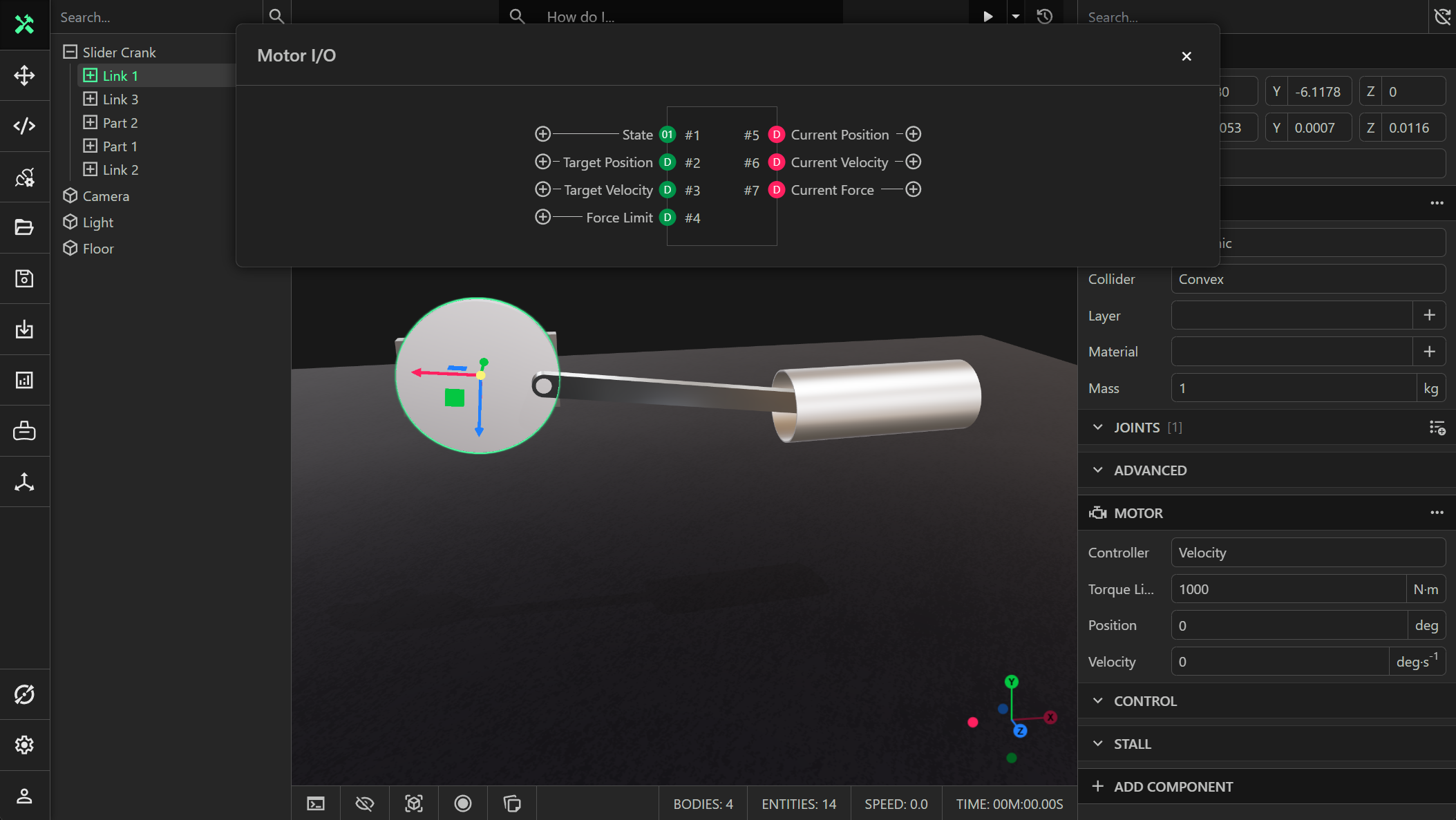
State
A boolean writable (input) signal that has the value true if the motor is powered on, and false otherwise.
Target Position
A double writable (input) signal that stores the target position for the controller.
Target Velocity
A double writable (input) signal that stores the target velocity for the controller.
Force Limit
A double (writable) input signal that stores the maximum force/torque that the motor can produce.
Current Position
A double (readable) output signal that stores the current position achieved by the motor.
Current Velocity
A double (readable) output signal that stores the current velocity achieved by the motor.
Current Force
A double (readable) output signal that stores the current force/torque applied by the motor.